It is an acronym that stands for “Non-Fungible Token”. What does it mean? Compared to fungible goods, such as banknotes (which can be exchanged for other banknotes of the same value), non-fungible goods indicate that these goods are not replicable and replaceable, because they possess a specific individuality.
In recent months, there has been a lot of talk about Non-Fungible Token , more commonly called NFT. The news of millionaire purchases, coupled with public criticism and poor understanding of the true nature of NFTs, have created more than a few prejudices in people. A little bit of what happened with the birth of cryptocurrencies.
This article has the goal – challenging to achieve, we admit – to explain in a few lines what NFTs are and what their role is in our life, especially that of tomorrow.
Let’s start with the basics: what are NFTs?
It is an acronym that stands for “Non-Fungible Token.” What does it mean? Compared to fungible goods, such as banknotes (which can be exchanged for other banknotes of the same value), non-fungible goods indicate that they are not replicable and replaceable because they possess a specific individuality.
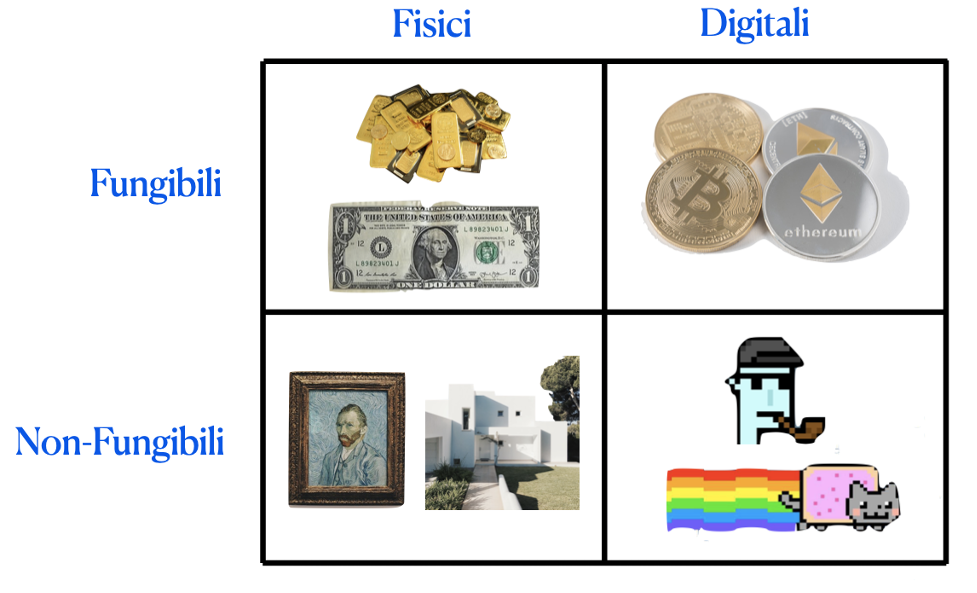
This individuality is given by a digital brand endowed with a certificate of authenticity and uniqueness. This certificate is issued thanks to blockchain technology. The NFTs are therefore associated with digital content. They guarantee the characteristics of uniqueness and authenticity, giving the owner a certificate of the genuineness of the digital product in question and owned by the NFT. Each NFT, thanks to the blockchain, is a unique piece, and therefore it is not fungible, i.e., not interchangeable. This is – in a nutshell – an NFT.
The numbers of NFTs
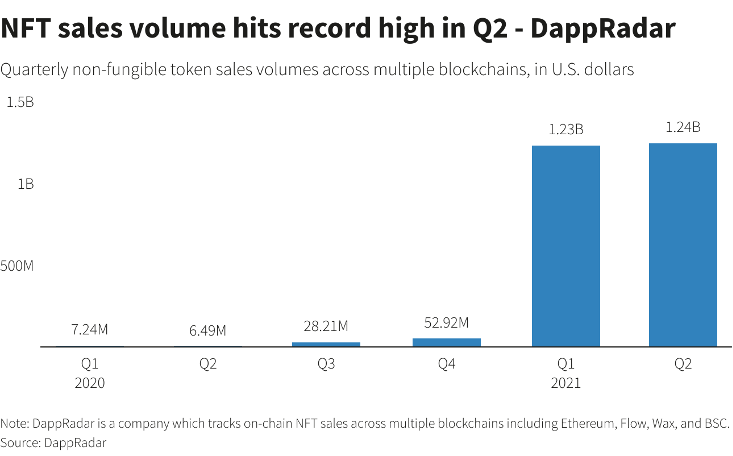
Currently, NFT sales have skyrocketed to $ 10.7 billion in the third quarter of 2021. This boom can also be attributed to COVID-19, which has prompted many people to experience digital differently: a second life. Furthermore, many artists, performers, and musicians – among the categories most affected by the pandemic – found themselves in the situation of reinventing themselves, finding in NFTs a way to earn from their work even remotely.
In fact, NFTs solve basic needs. First of all, giving value to what previously had none: digital art and the rights of creators on it. Secondly, the need for “recognition” (social, economic) of people also in digital spaces (and thanks to digital assets) is currently not satisfied.
To satisfy this need, dozens of metaverses have been created, where users can use and show off their NFTs. Facebook’s announcement of wanting to launch its own metaverse is a clear sign that the road to virtual worlds in which to use one’s NFTs is now open.
But what is a metaverse? The canonical definition is a three-dimensional space where individuals can move, share and interact through personalized avatars. In truth, there is no univocal definition. Still, it generically indicates a virtual place where you can hang out with other people, interact, invest and create your own character in the image and likeness of what you want to be.
The advantages of NFTs: why create and sell them?
NFTs are a godsend for brands and creators if you can say so. A whole new billionaire market born out of nothing in recent years: the earning possibilities are practically unlimited, and the costs for companies and individuals are minimal.
The application fields are equally infinite: everything can be sold as NFT, just create a digital copy of what you want to sell, and that’s it. You can tokenize individual products or digital works of art or create collections of thousands of objects.
Furthermore, NFTs incorporate all the classic advantages of the blockchain, namely decentralization, disintermediation, immutability of the register, traceability, and verifiability of its contents, movements, and transfers.
Another advantage is the possibility of earning from second, third, fourth, etc., sales. level: in a nutshell, you are paid back for your rights every time your NFT is resold to a third party. All thanks to the fact that every transfer of ownership is traceable on the blockchain on the blockchain. A continuous revenue stream, unlimited over time.
Too much power to intermediaries
However, a limitation of NFTs is that today it is necessary to interface with numerous intermediaries. In fact, a brand or creator wishing to create and sell their NFTs must necessarily contact two third parties: the blockchain, on which to mine their token, and a marketplace, where they can sell it.
While there is little to do with the blockchain, a solution to do without third-party marketplaces – which earn thanks to commissions – exists, and it is NFT-Commerce, our digital commerce platform dedicated only to NFTs. Through our system, we will allow you to create a direct connection between your site/app with the reference blockchain, either through a dedicated wallet or directly with a payment gateway via credit card.
Therefore, the user can directly buy your NFTs on your digital property, either through their own cryptocurrency or by paying by card. This system allows both to save third-party commissions, manage the shopping experience, and recover customer data.
Conclusions: why selling NFT makes you money
NFTs are the future – it is undeniable – because they respond to needs long been neglected by institutions and companies. Exploring this world can bring significant gains and offer a competitive advantage over competing companies.
It is crucial to consider the advantages and the challenges that new technology poses and not fall into the trap of superficiality when approaching NFTs. This is why it is essential to ask for support from those who already live and work in the world of blockchain. Because when a new market arises, relying on those who have already managed to create expertise is fundamental.
Sign up for our newsletter now!







